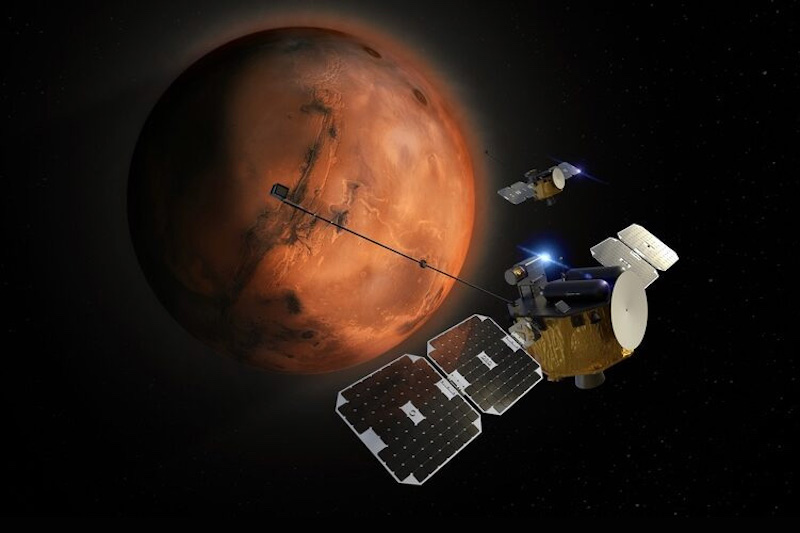
Mars mission to review magnetosphere on a budget
NASA and its companions need to discover out if they will research the photo voltaic system with out breaking the financial institution. To this finish, they’ll quickly ship a brand new, cost-effective Mars mission to the pink planet. A pair of small satellites – referred to as Blue and Gold – will fly into Earth orbit no sooner than spring 2025. They’ll finally go on an 11-month journey to Mars.
This 5-month mission to the pink planet is formally referred to as the Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers, or ESCAPADE. It represents a proof of idea, counting on new spaceflight expertise to maintain prices down. Mission chief Robert Lillis beforehand stated in a chat with UC Berkeley Information:
ESCAPADE and two different NASA missions lately authorized are experiments to see whether or not advances within the area trade over the past 5 to 10 years can translate to a a lot better bang for the buck when it comes to science per greenback. Sending two spacecraft to Mars for the full value of beneath $80 million is simply extraordinary. However present NASA management is taking the danger.
The danger is a mission failure. However at 10% the traditional value for sending a spacecraft to Mars, NASA figures it might afford to roll the cube. Lillis put it this fashion:
As a substitute of spending $800 million for a 95% probability of success, can we spend $80 million for an 80% probability? That is what NASA is looking for out with these missions, and we’re fortunate to be one of many guinea pigs.

Going for the Gold and Blue on Mars
Lillis can also be the College of California, Berkeley Area Sciences Laboratory (SSL) affiliate director for planetary science and astrobiology. The SSL – working along side NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Heart – engineered the dual probes. In managing the mission, the SSL will run the onboard devices and course of the info. It’s additionally flying the craft.
And in order that’s why the satellites are named Gold and Blue. They’re the official Berkeley colours. Sending two satellites to scan the identical terrain will give ESCAPADE’s information an added dimension. Lillis stated:
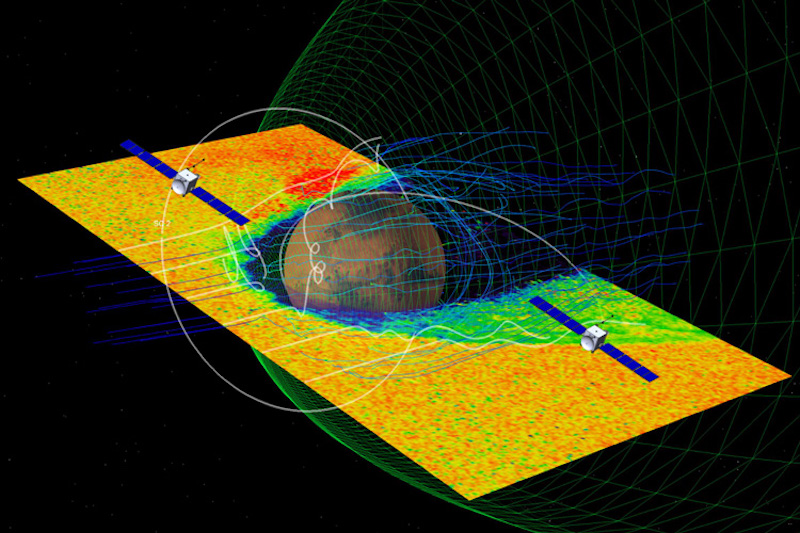
With simultaneous two-point observations of the photo voltaic wind and Mars’ ionosphere and magnetosphere, ESCAPADE will carry us the primary stereo image of this extremely dynamic plasma setting.
Determining how Mars will get electrically charged
The Mars mission goals to trace the interior workings of the planet’s magnetic setting, aka its magnetosphere. The mission scientists need to understand how vitality and matter from the photo voltaic wind makes its manner out and in of Mars’ planetwide magnetic area.
Mars’ magnetic area is not like these on different planets. It’s typically referred to as a hybrid. On the one hand, it’s a solar-induced magnetosphere, like that on Venus, created partly by the interplay of the photo voltaic wind with the Martian environment. However, it additionally has localized areas of intrinsic magnetic fields from the planet’s crust. Plus there are larger-scale international influences.
NASA described the mission targets for probes:
ESCAPADE will analyze how Mars’ magnetic area guides particle flows across the planet, how vitality and momentum are transported from the photo voltaic wind by means of the magnetosphere and what processes management the circulate of vitality and matter into and out of the Martian environment.
ESCAPADE is a part of the NASA Small Progressive Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program. The spacecraft is comparatively small, with a mass beneath 200 kilos (90 kg). Onboard are a magnetometer, an electrostatic analyzer to measure superthermal ions and electrons and a plasma density probe.
The tip of the mission is deliberate for March 2027.
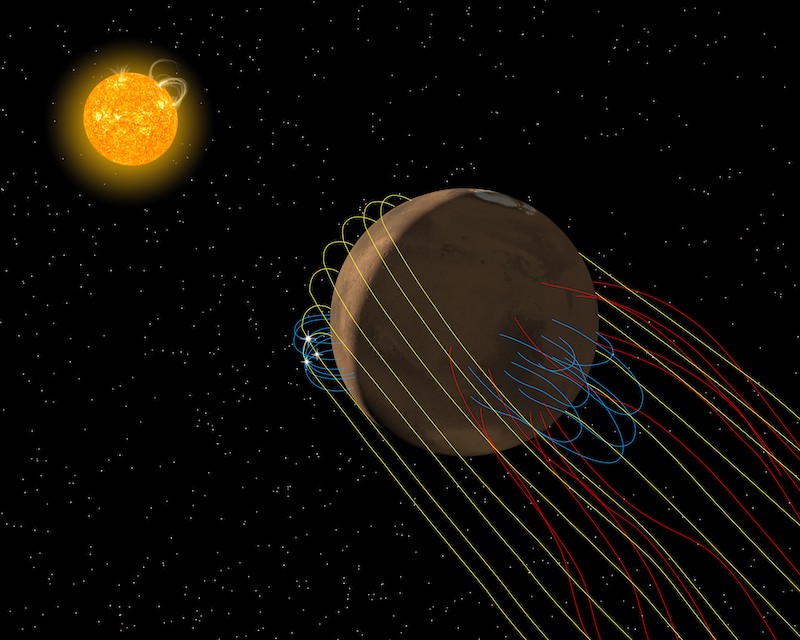
Backside line: The Mars ESCAPADE mission will research the pink planet’s magnetosphere utilizing a pair of small satellites. ESCAPADE will launch no sooner than spring 2025.
Learn extra: Mars in 2024: Discover it within the morning sky

