Utilizing the James Webb Area Telescope, astronomers have captured a shocking picture of a distant supernova in a galaxy that appears prefer it’s being stretched like heat taffy.
Nonetheless, the golden smear hiding this gravitationally lensed supernova, which has been nicknamed “supernova Hope,” is not simply exceptional for its aesthetic worth. The supernova, which exploded when the 13.8-billion-year-old universe was simply round 3.5 billion years outdated, tells us one thing about an enormous downside in cosmology referred to as the “Hubble stress.”
The Hubble stress comes from the truth that scientists cannot agree on the precise fee of growth of the universe, dictated by the Hubble fixed. Mainly, the speed may be measured ranging from the native (and subsequently latest) universe, then going farther again in time — or, it may be calculated ranging from the distant (and subsequently early) universe, then working your manner up. The difficulty is each strategies ship values that do not agree with one another. That is the place the James Net Area Telescope (JWST) is available in.
Gravitationally lensed supernovas within the early cosmos the JWST is observing might present a 3rd manner of measuring the speed, probably serving to resolve this “Hubble hassle.”
“The supernova was named ‘supernova Hope’ because it provides astronomers hope to raised perceive the universe’s altering growth fee,” Brenda Frye, examine group chief and a College of Arizona researcher, stated in a NASA assertion.
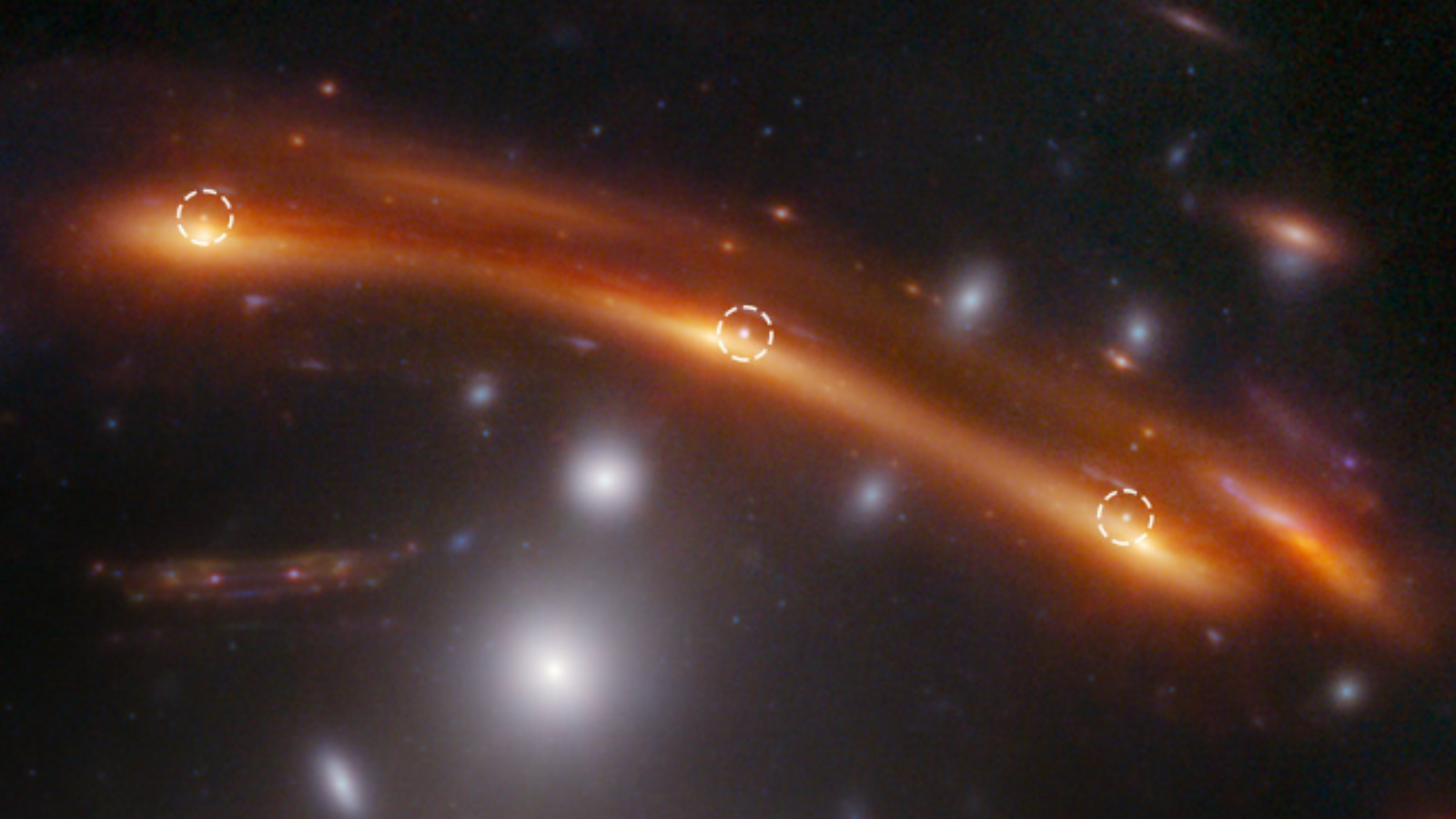
This investigation of supernova Hope started when Frye and her world group of scientists discovered three curious factors of sunshine in a JWST picture of a distant, densely packed cluster of galaxies. These factors of sunshine within the picture weren’t seen when the Hubble Area Telescope imaged the identical cluster, often called PLCK G165.7+67.0 or, extra merely, G165, again in 2015.
Associated: Bizarre physics on the edges of black holes could assist resolve lingering ‘Hubble hassle’
“It began with one query by the group: ‘What are these three dots that weren’t there earlier than? May that be a supernova?'” Frye stated. “Preliminary analyses confirmed that these dots corresponded to an exploding star, one with uncommon qualities.”
The house surrounding G165 was chosen for the PEARLS program as a result of it’s within the midst of “starburst,” a interval of intense star formation, and spawning 300 photo voltaic plenty of stars per 12 months. Such excessive star formation charges are correlated with increased cases of supernova explosions.

Supernova Hope is a particular sort of supernova referred to as a Kind Ia supernova. These supernovas happen in binaries that comprise a predominant sequence star, just like the solar, and a star that has exhausted its gasoline for nuclear fusion and has change into a lifeless husk, referred to as a white dwarf.
If these stellar our bodies are shut sufficient, then the lifeless star can act like a cosmic vampire, drawing plasma from the dwelling, or “donor,” star. As this continues, the fabric builds up till it triggers a thermonuclear explosion — explosions we see as Kind Ia supernovas. Due to how uniform their flashes of sunshine are, these supernovas are a wonderful device that astronomers can use to measure cosmic distances. Astronomers, subsequently, check with Kind Ia supernovas as “commonplace candles.”
A technique of getting a price for the Hubble fixed is to take a look at Kind Ia supernovas within the native universe to measure their distances from us, and from each other, after which measure how briskly they’re receding. The opposite predominant strategy of measuring the universe’s growth includes taking observations of the distant universe, then calculating how briskly the cosmos is increasing by deduction.
However, once more, these strategies aren’t in settlement. Supernova Hope, nevertheless, might act as a bridge between the 2 methods.
Einstein lends a hand
Gravitational lensing is an impact predicted in Albert Einstein’s magnum opus idea of gravity, which was created in 1915 and is named “normal relativity.”
Basic relativity means that objects with mass trigger the warping of spacetime, the four-dimensional unification of house and time, with gravity arising from this curvature. The higher the mass of the item, the extra excessive the warping of house and, thus, the higher the gravitational affect that object has. That is what causes moons to orbit planets, planets to orbit stars, and stars to orbit supermassive black holes.
This warping of spacetime has one other fascinating impact, too. When mild passes an object with a robust warping affect, an object we’ll now name a “gravitational lens,” the sunshine’s path will get bent across the object’s warp. The trail the sunshine takes is dependent upon how shut it will get to the gravitational lens.
Which means mild from the identical object can take paths bent to completely different levels and with completely different lengths. Subsequently, that mild can arrive at telescopes just like the JWST at differing occasions. That is how a lensed background object can appear “smeared” like taffy or seem in a number of locations in the identical picture.
That is what is occurring to supernova Hope on this picture as its mild passes the gravitational lens G165.
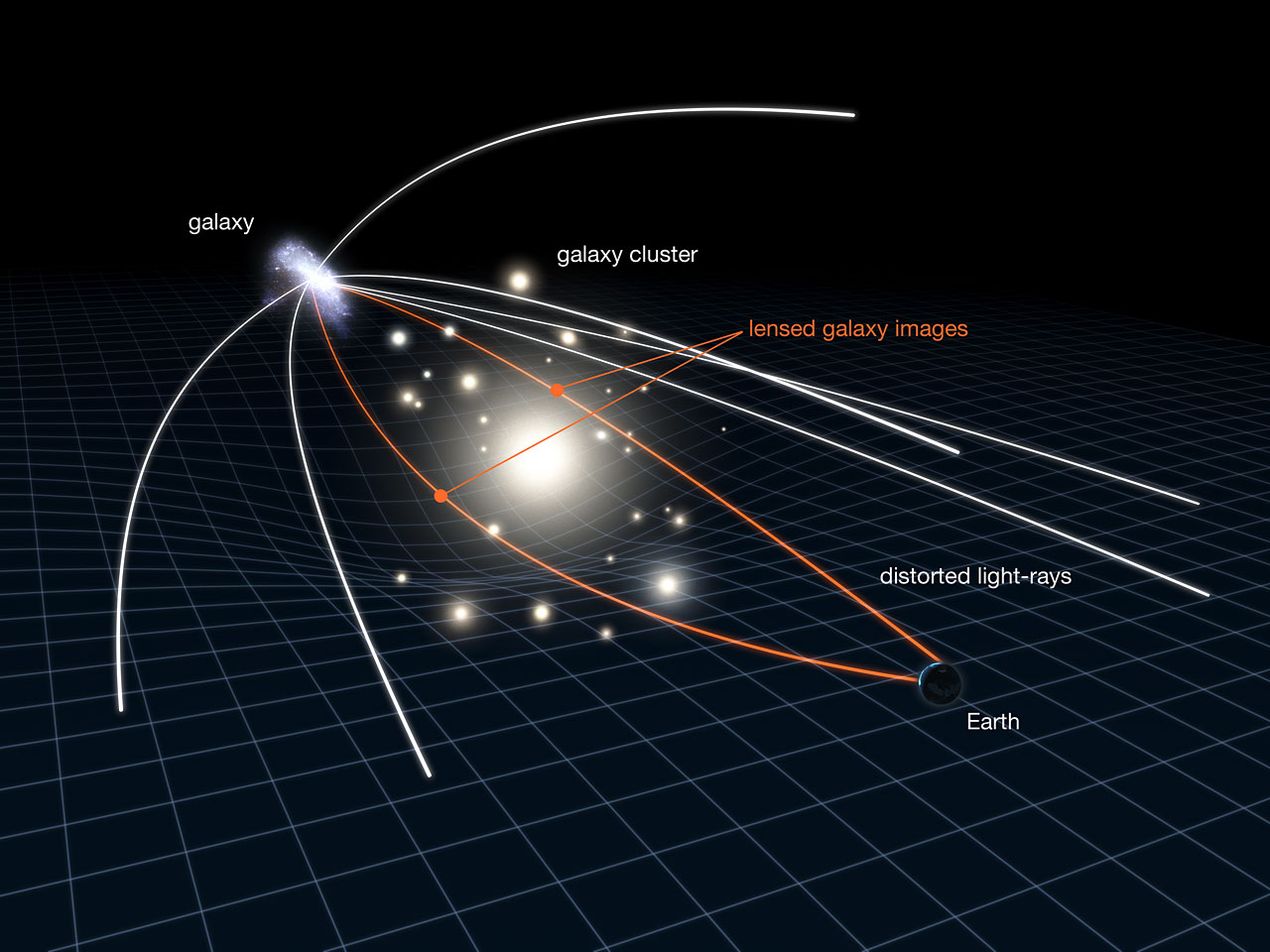
“Gravitational lensing is necessary to this experiment. The lens, consisting of a cluster of galaxies that’s located between the supernova and us, bends the supernova’s mild into a number of photographs,” Frye stated. “That is much like how a trifold self-importance mirror presents three completely different photographs of an individual sitting in entrance of it.”
The College of Arizona researcher defined the impact was demonstrated proper earlier than the eyes of the group within the G165 JWST picture, the place the center supernova picture appeared flipped relative to the opposite two photographs.
“To realize three photographs, the sunshine traveled alongside three completely different paths. Since every path had a unique size, and lightweight traveled on the similar pace, the supernova was imaged on this JWST remark at three completely different occasions throughout its explosion,” Frye continued. “Within the trifold mirror analogy, a time delay ensued wherein the right-hand mirror depicted an individual lifting a comb, the left-hand mirror confirmed hair being combed, and the center mirror displayed the individual placing down the comb.
“Trifold supernova photographs are particular. The time delays, supernova distance, and gravitational lensing properties yield a price for the Hubble fixed.”

The group adopted up on supernova Hope with the JWST in addition to some Earth-based devices, together with the MMT 6.5-meter telescope on Mount Hopkins and the Massive Binocular Telescope on Mount Graham, each positioned in Arizona.
This led the group to substantiate that supernova Hope is anchored to a background galaxy nicely behind the lensing cluster G165. Mild from the cosmic explosion has been touring to Earth for 10.3 billion years, which means this white dwarf blew its high simply 3.5 billion years after the Huge Bang.
“A distinct group member made one other time delay measurement by analyzing the evolution of its mild dispersed into its constituent colours or ‘spectrum’ from the JWST, confirming the Kind Ia nature of supernova Hope,” Frye stated. “Supernova Hope is likely one of the most distant Kind Ia supernova noticed so far,”
Regardless of current within the early universe, the worth of the Hubble fixed delivered by the observations of supernova Hope appears to correspond with measurements of different commonplace candles within the native universe, thus disagreeing with measurements of different objects within the early universe.
“Our group’s outcomes are impactful,” Frye concluded. “The Hubble fixed worth matches different measurements within the native universe and is considerably in stress with values obtained when the universe was younger. JWST observations in Cycle 3 will enhance the uncertainties, permitting extra delicate constraints on the Hubble fixed.”
The group’s analysis is within the strategy of being peer-reviewed earlier than publication.

