This easy science demonstration is a incredible strategy to study volcanoes, tectonic plates and convection currents.
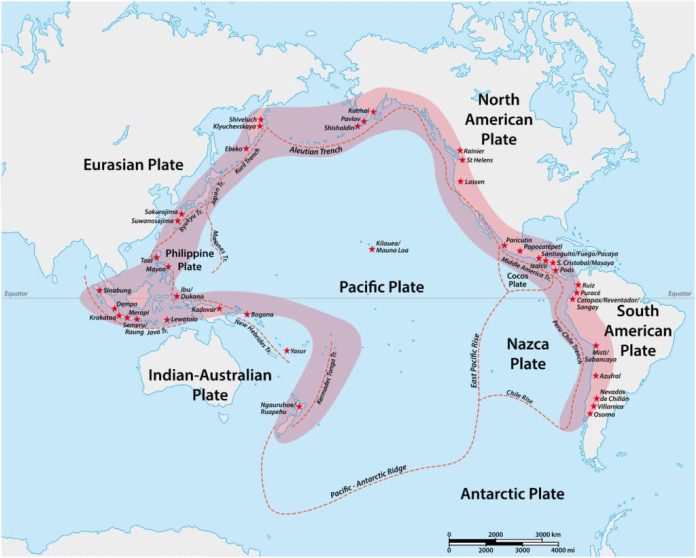
Volcanoes are principally discovered on tectonic plate boundaries as a result of the motion of tectonic plates permits magma to succeed in the floor. The Ring of Hearth across the Pacific Plate is house to round 75% of the world’s volcanoes!
Volcanoes type in three areas:
- constructive plate boundaries
- harmful play boundaries
All three settings are locations the place magma is ready to escape by means of gaps within the Earth’s crust.
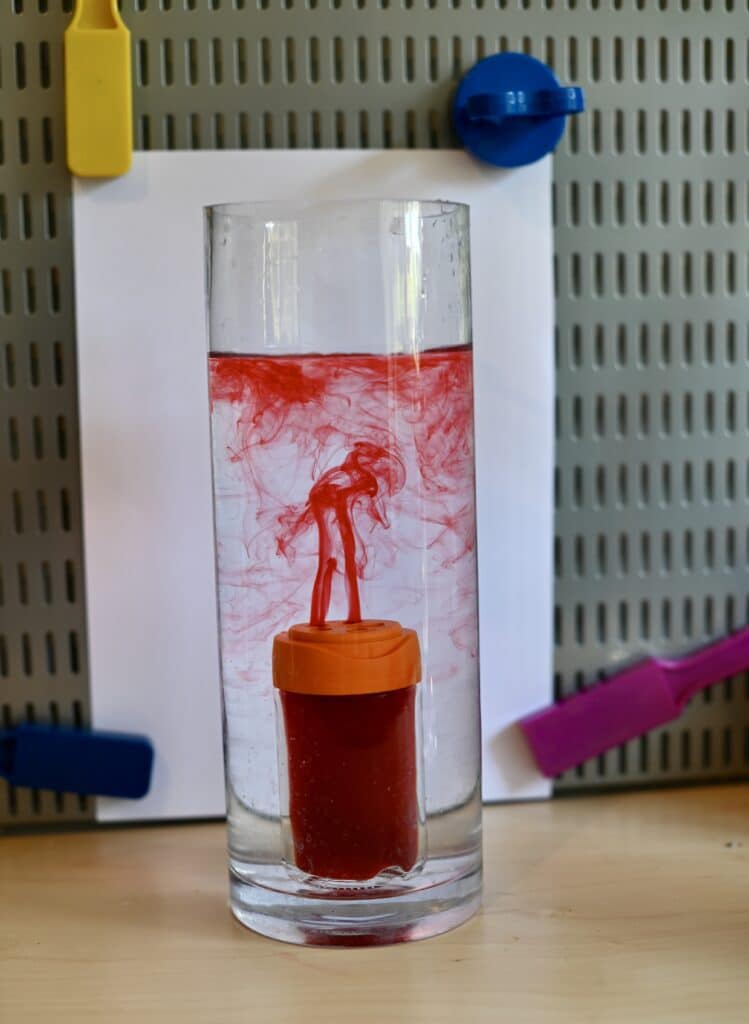
This underwater volcano science demonstration exhibits how convection currents work. Convection currents enable scorching magma to stand up by means of the mantle to the Earth’s crust.
Methods to make an underwater volcano
You’ll want
A big jar
Chilly water
Scorching water
Meals colouring
Small conical flask or spice jar
Directions for an Underwater Volcano
Fill the massive jar, about ¾ full, with chilly water.
Rigorously ( ask an grownup to assist ) fill the smaller container near the highest with scorching water and add just a few drops of meals colouring.
Rigorously decrease the small container into the massive jar. Watch as the nice and cozy, colored water rises up into the cooler water above.
When you’re utilizing a spice jar with small holes, you’ll must shake the jar a bit of to permit any air bubbles to flee.
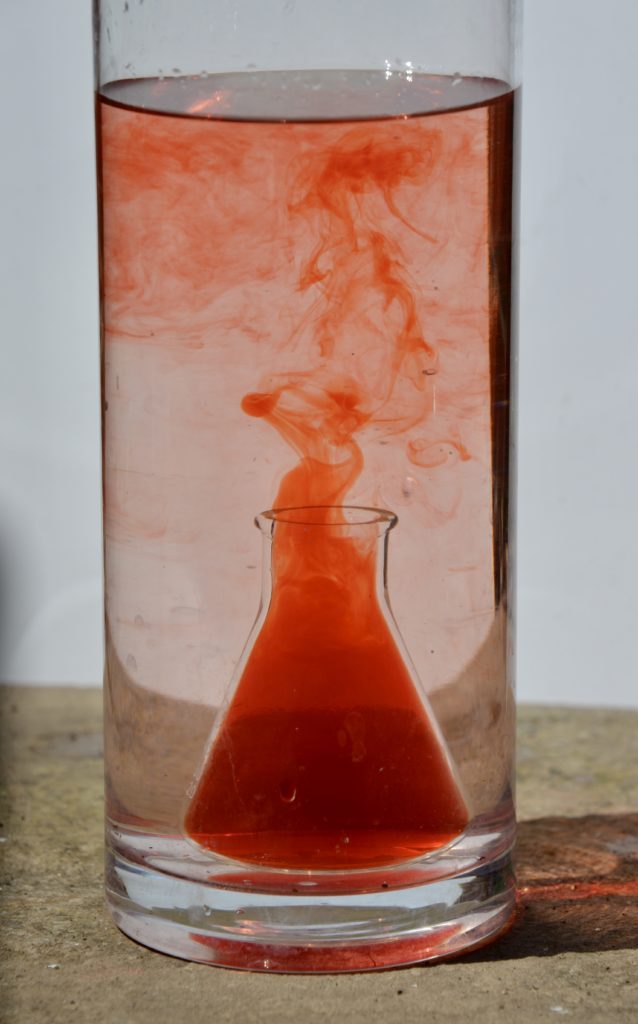

What’s a convection present?
A convection present is how warmth rises and falls in liquids and gases. When a liquid or fuel is heated, the particles transfer sooner than when they’re chilly. The area between particles will increase, making the density lower. The nice and cozy, much less dense liquid or fuel rises upwards, and cooler, denser liquids or gases fill the area. This results in a convection present as the method is repeated time and again.


Convection currents and plate tectonics
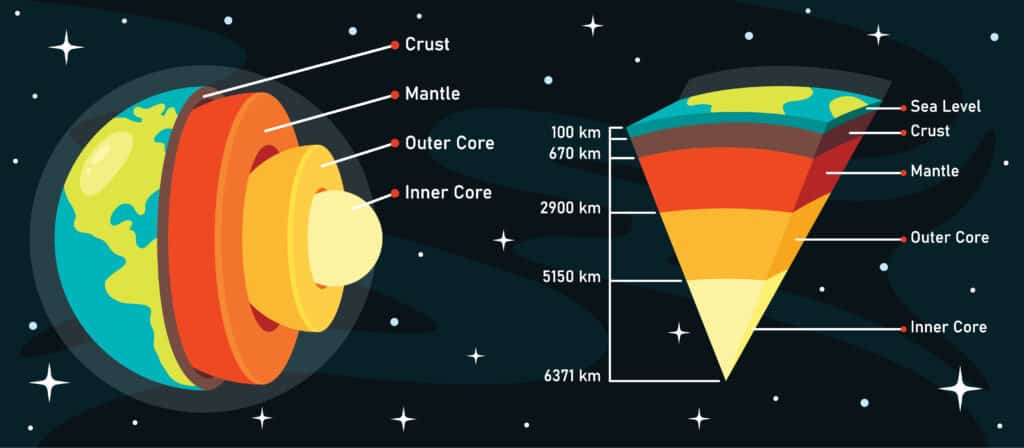
Convection currents play an necessary function within the motion of magma within the Earth’s crust and mantle layers. Warmth from the Earth’s core warms the magma closest to it. The new magma rises up by means of the mantle, cools because it will get nearer to the crust and sinks once more. This can be a convection present. Because the magma sinks, it might probably transfer tectonic plates throughout the floor of the Earth.
This motion of tectonic plates results in cracks or fissures within the floor, permitting magma to succeed in the Earth’s floor, and is why most volcanoes are discovered at plate boundaries.
Tectonic Plate Boundaries
Constructive plate boundaries
Constructive plate boundaries ( divergent ) type the place convection currents transfer plates aside. Because the plates transfer aside, magma rises up from the earth’s mantle layer to fill the hole. The magma cools on the floor, forming igneous rock. The method ultimately results in the formation of ridges and rifts. If magma erupts onto the floor, defend volcanoes can type.
If this course of occurs between continental plates, it creates deep, extensive valleys on land. When it happens between oceanic plates, it results in a mid-ocean ridge. Examples of mid-ocean ridges embody the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge, East Pacific Rise and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Volcanoes are sometimes discovered alongside mid-ocean ridges.
Such a plate boundary can also be known as divergent.
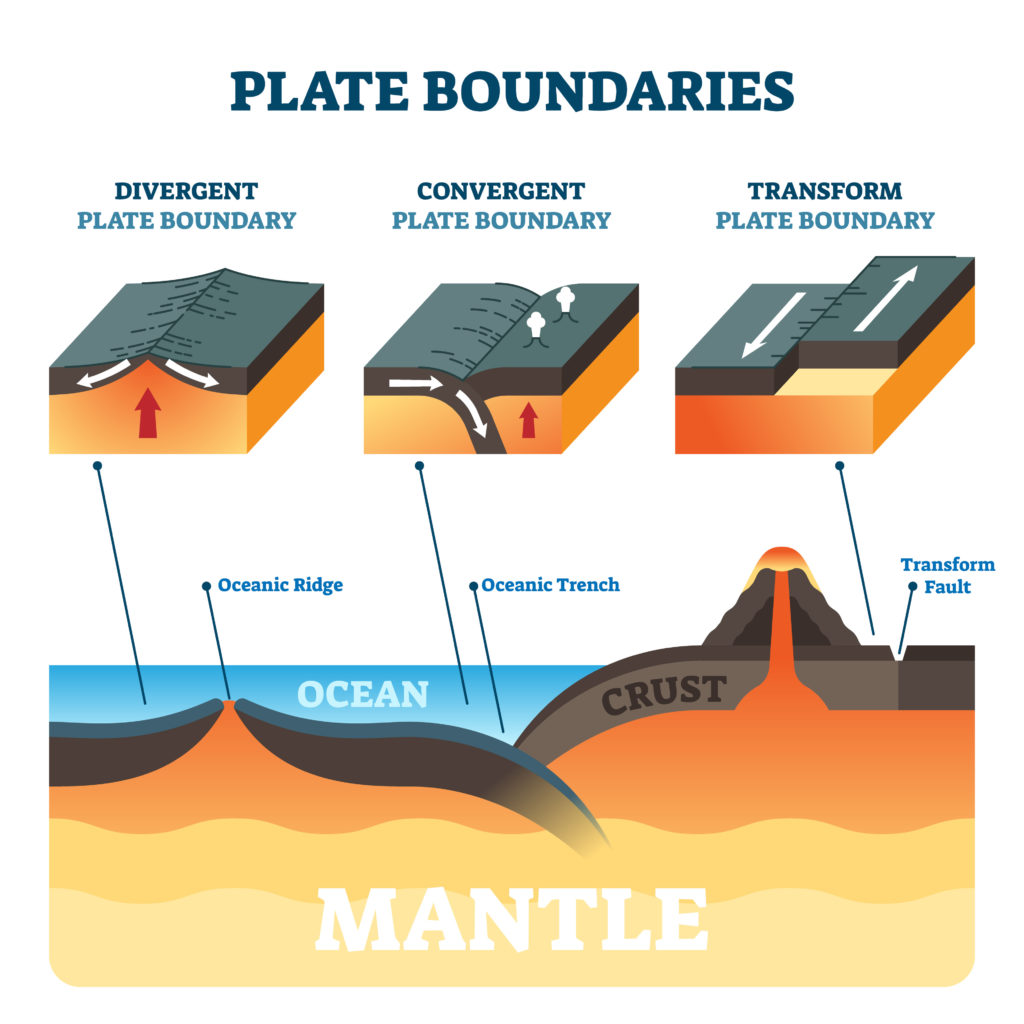
Harmful plate boundaries
Harmful plate boundaries ( convergent ) type the place convection currents push tectonic plates collectively. There are three forms of harmful plate boundaries.
- oceanic plate and oceanic plate
- oceanic plate and continental plate
- continental plate and continental plate
Continental and oceanic
Oceanic plates are denser than continental plates. Which means the oceanic plate is pressured underneath the continental plate after they transfer in direction of one another. That is known as subduction. Oceanic trenches, for instance, the Mariana Trench, type when an oceanic plate is pressured down underneath a continental plate. The oceanic plate melts attributable to friction and warmth from contained in the Earth to type magma, inflicting earthquakes. This is named a subduction zone.
Magma collects in a magma chamber, which then rises up by means of cracks within the continental crust. If sufficient stress builds up, volcanic eruptions can happen, creating volcanoes.
Oceanic plate and oceanic plate
When two oceanic plates collide, the densest plate is pushed down, resulting in subduction. The subducted plate melts, creating magma. When the magma comes into contact with the ocean, it cools shortly to type a sequence of volcanoes known as an island arc.
Continental plate and continental plate
When two continental plates collide, they don’t subduct. As an alternative, the plates are pressured upwards, creating mountains. The collisions could cause earthquakes however not volcanoes.
Such a plate boundary can also be known as convergent.
Rework plate boundaries
A remodel ( or conservative ) boundary is the place tectonic plates transfer previous one another. Volcanoes aren’t normally discovered at one of these plate boundary. The San Andreas Fault, which runs by means of most of California, is an instance of one of these plate boundary.
Scorching Spots
Scorching spots are areas the place warmth from superheated magma causes the crust above to soften and skinny. This enables magma to flee to the floor, forming a volcano. These kind of volcanoes are known as defend volcanoes. They’re flatter than different forms of volcanoes.
Mount Erebus in Antarctica is an instance of one of these volcano.
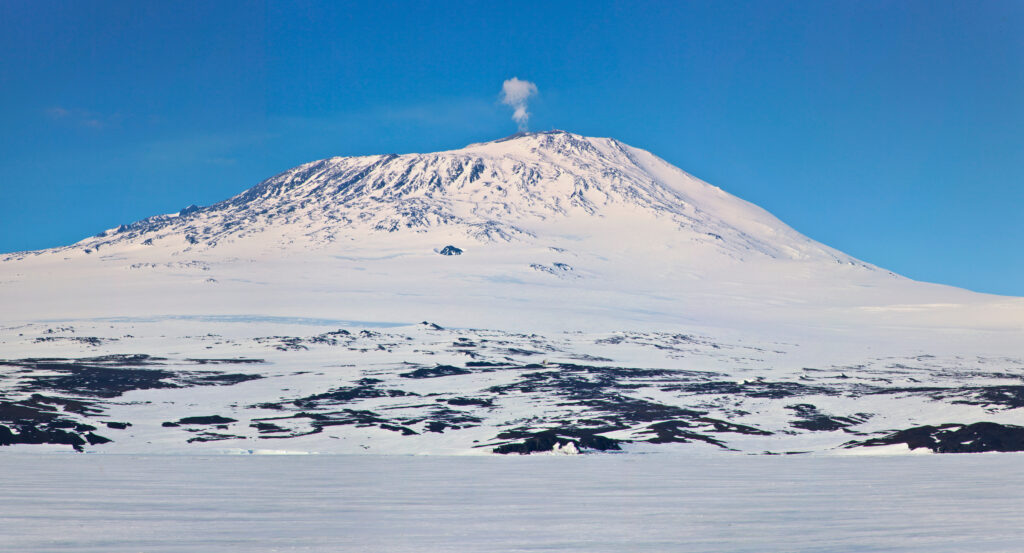

Extra real-life examples of convection currents
Radiators and fires
Scorching air rises from warmth sources comparable to fires or radiators. When air close to a fireplace or radiator is heated, it expands, turns into much less dense and rises upwards. Cooler, denser air replaces the nice and cozy air, which is then heated, turns into much less dense and rises. The method continues transferring warmth across the room containing the warmth supply.
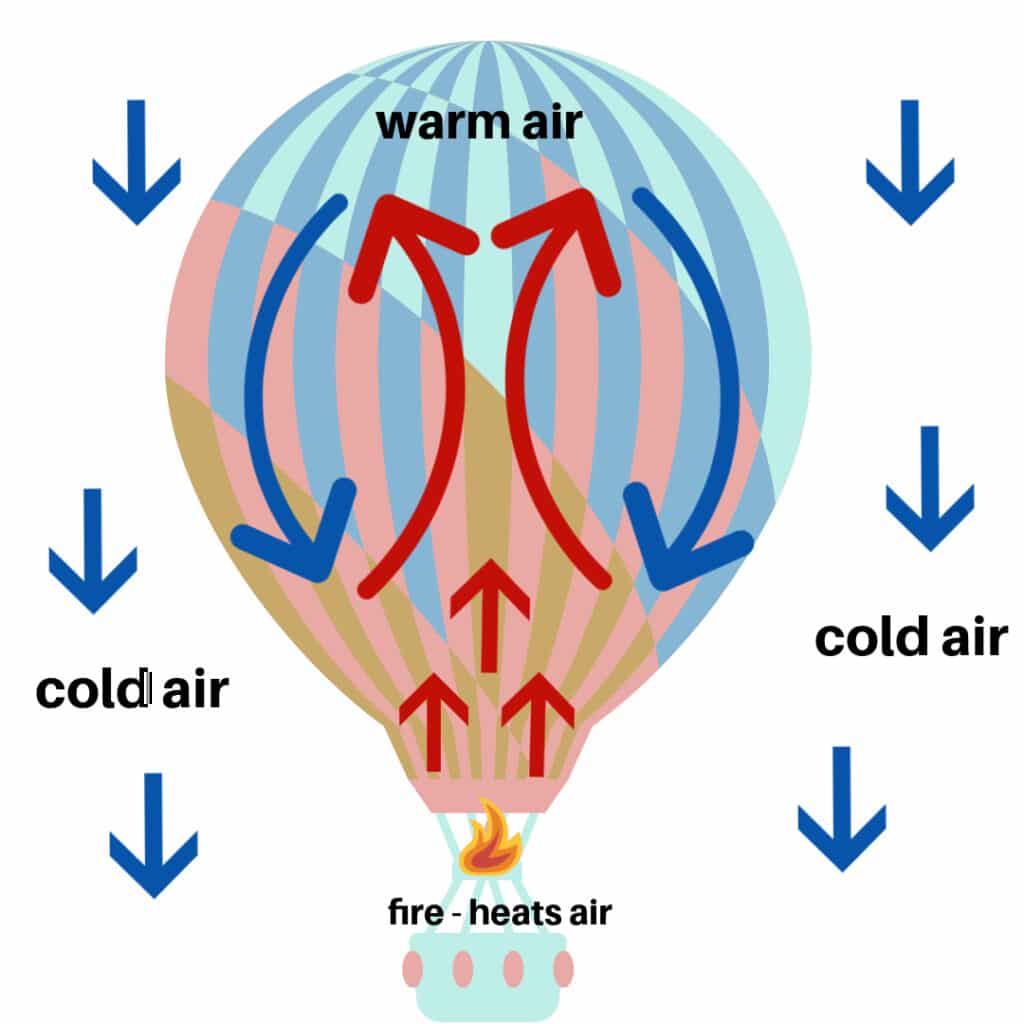
Scorching Air Balloons
A convection present heats the air contained in the balloon, making the nice and cozy air contained in the balloon much less dense than the cooler air on the surface. This causes the recent air balloon to rise upwards.
Heating water in a pan
Heating water in a pan is one other real-life instance of a convection present.
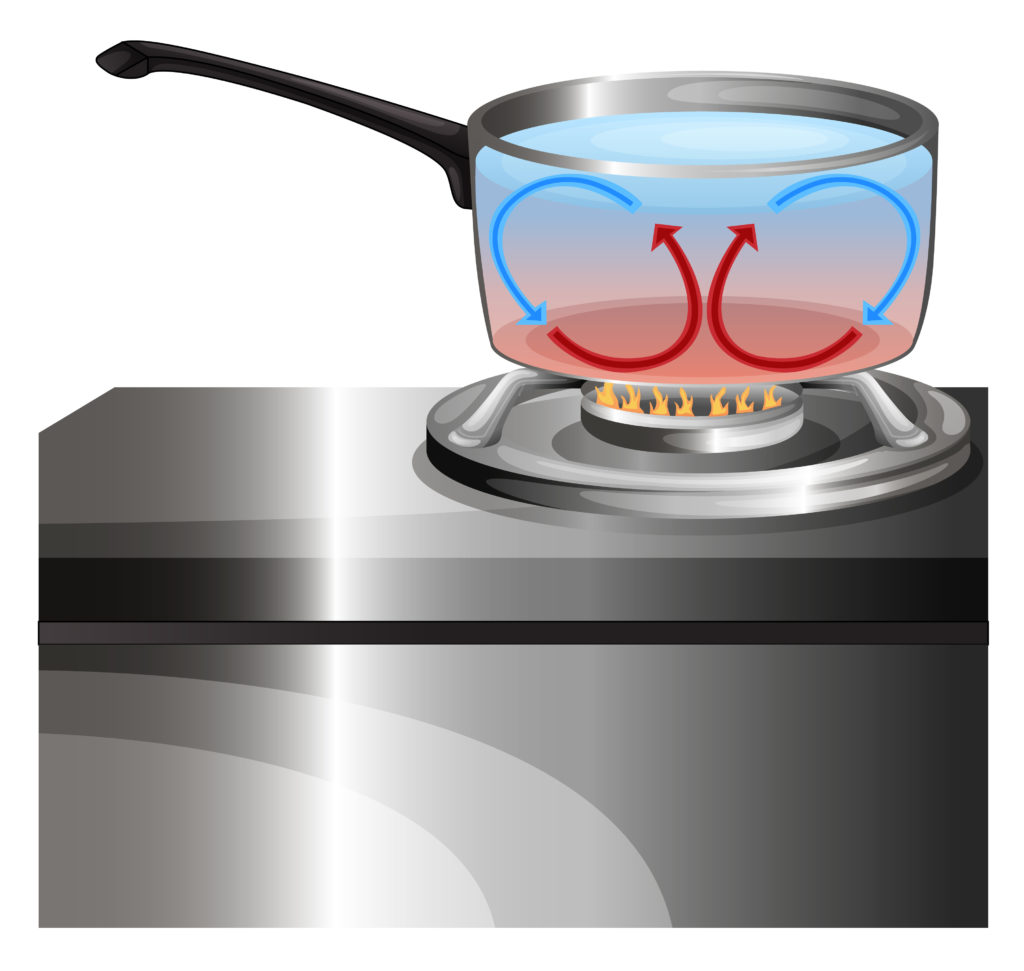

Convection currents additionally trigger sea breezes and most different winds.

Extra volcano science actions for youths
Make a mannequin seismometer to learn the way scientists detect earthquakes.
Study tectonic plates with an orange.
Create a playdough mannequin of the Earth’s totally different layers.
Make a baking soda volcano.
Examine latest volcano exercise around the globe with NASA.
Science ideas
Convection currents
Tectonic plates
Seismometer
Final Up to date on Could 24, 2024 by Emma Vanstone