
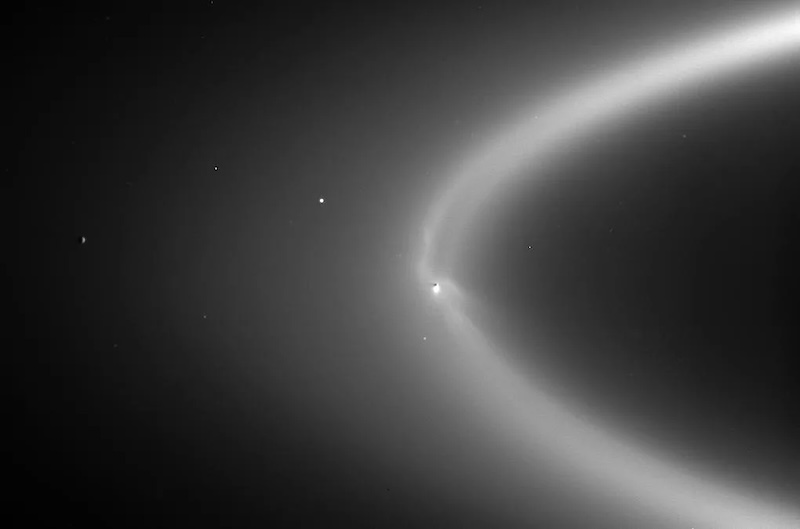
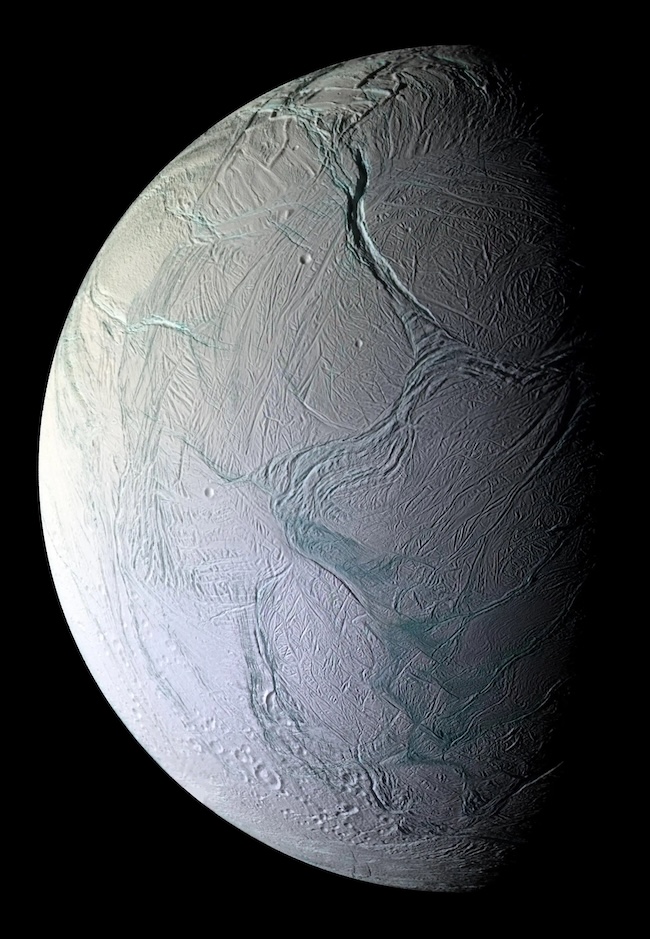
- Saturn’s moon Enceladus has an ocean underneath its icy floor. Geyser-like plumes of water vapor erupt via cracks within the ice crust and into area.
- NASA’s Cassini spacecraft sampled the plumes because it flew via them a number of instances. It discovered natural molecules and different proof that the ocean is doubtlessly liveable.
- Much more advanced organics have now been recognized within the plume materials. Researchers in Germany discovered them in a brand new evaluation of Cassini’s knowledge.
Intriguing new evaluation of Cassini’s knowledge
The probabilities for all times on Saturn’s ocean moon Enceladus preserve enhancing. Research utilizing knowledge from NASA’s Cassini mission proceed to indicate situations within the subsurface ocean look like liveable, no less than for microbes. On September 11, 2024, researchers in Germany on the Europlanet Science Congress stated they accomplished a brand new research of natural molecules on Enceladus. They stated they’ve discovered proof for added and beforehand unknown advanced natural molecules and chemical teams. The chemical teams are frequent to many organic molecules, no less than on Earth. It isn’t proof of life but, nevertheless it’s one other huge clue supporting the likelihood.
Nozair Khawaja on the Free College of Berlin in Germany, who led the research, offered the summary. And New Scientist reported the most recent findings on September 13, 2024.
Scientists have thought of Enceladus as a potential candidate for all times ever since Cassini confirmed it has a subsurface ocean. That rivalry has grown as ongoing research of the Cassini’s knowledge have revealed the ocean to be doubtlessly liveable in a number of methods. Because the summary said:
The seek for liveable environments within the outer photo voltaic system is on the forefront of latest area exploration. The presence of subsurface liquid water, vitality sources and natural molecules make some icy moons with subsurface oceans potential websites to seek for extraterrestrial life. Amongst these our bodies are the Jovian moon Europa and the Saturnian moons Enceladus and Titan. The latest detection of phosphorus (Postberg et al. 2023) and HCN [hydrogen cyanide] (Peter et al. 2024) within the ocean of Enceladus has additional enhanced its astrobiological potential.
Complicated organics on Enceladus revealed
The researchers studied knowledge from the Cassini spacecraft. Cassini explored Saturn and its moons in unprecedented element. It ended its mission on September 15, 2017. The spacecraft flew via the water vapor plumes on Enceladus a number of instances, analyzing their composition. It additionally analyzed particles from the plumes that had ended up in Saturn’s E ring. Certainly, Cassini discovered all six of the chemical components that life requires (no less than life on Earth): carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus and sulfur. It additionally discovered different less complicated natural molecules within the plumes.
Now, the brand new research has revealed much more natural molecules and chemical substances than what scientists beforehand knew. These embrace esters, alkenes and ethers, in addition to different advanced molecules containing nitrogen and oxygen. We don’t know but precisely which chemical teams the organics originated from. However their presence supplies proof for potential chemical reactions that might produce fat or nucleotide bases, the constructing blocks of DNA. The summary said:
Our outcomes verify the presence of aryl and oxygen moieties [molecule parts] in ice grains that have been beforehand sampled within the E ring, offering contemporary insights into the soundness of those compounds at Enceladean hydrothermal websites. As well as, mass spectra of those freshly ejected organic-bearing grains additionally exhibit sure spectral options that weren’t noticed at decrease influence speeds within the E ring. For the primary time, we discover ether/ethyl and ester/alkene group moieties in these plume ice grains that present a foundation for alterative pathways for natural synthesis in hydrothermal programs on Enceladus, which carries important implications for the habitability of the Enceladus ocean.
Analyzing particles in plumes and E ring
Cassini analyzed tiny ice grains and different particles in Saturn’s E ring that originated from the water vapor plumes on Enceladus. As well as, it additionally immediately analyzed particles within the plumes themselves. Earlier research of the Cassini knowledge had centered totally on the ring particles. The paper affirmed:
Enceladus ejects subsurface materials into area within the type of ice grains and vapors from the moon’s south polar area. A lot of the ice grains fall again onto the floor, with solely a fraction of those grains escaping the moon’s Hill Sphere and forming a part of Saturn’s E ring. Cassini’s on-board mass spectrometers – the Cosmic Mud Analyzer (CDA) and Ion and Impartial Mass Spectrometer (INMS) – sampled gasoline and ice grains each from the plume and within the E ring.

Organics in freshly ejected ocean spray
The summary continued:
Up to now, natural materials has solely been topic to detailed investigation by CDA in E ring ice grains. Right here, for the primary time, we analyze natural materials in freshly ejected Enceladus plume ice grains. For this function, Cassini’s flybys of the Enceladus plume offered a singular alternative for CDA to gather freshly ejected subsurface oceanic materials, significantly natural compounds, versus settled E ring grains.
On this new research, the researchers have been primarily within the plume particles within the “ocean spray” itself. Apparently, these newly recognized natural molecules hadn’t been discovered earlier than within the particles within the E ring. The researchers stated this was as a result of the ice grains within the plumes truly contained much less water than these within the rings. This made it simpler to detect the extra advanced natural molecules.
There have been hints of them within the earlier evaluation that scientists had carried out, however not affirmation but, as Andrew Coates at College School London famous:
We knew already from evaluation that had been carried out earlier than that there have been heavier molecules, however that is going into extra element about precisely what they is perhaps.
Organics on Enceladus as indicators of life?
The detection of advanced organics isn’t proof of life, however it’s a important discovering, to make sure. The devices on Cassini weren’t designed to seek out life. However what they did discover is definitely tantalizing. Coates stated:
It wasn’t designed to truly search for life, however extra details about constructing blocks for all times is definitely one thing which can preserve us going for a while.
In actual fact, one other research from December 2023 confirmed that direct proof of life itself – if it exists – could possibly be discovered proper within the plumes themselves. That might seemingly require a follow-up mission, nevertheless it’s an thrilling risk.
Backside line: Scientists in Germany have discovered extra advanced organics on Enceladus, the ocean moon of Saturn. Are they proof for all times?
Learn extra: Enceladus internet hosting cell-sized particles, a touch of life?
Learn extra: The way to discover life on Enceladus? Look within the plumes

