Adaptive immunity is a key a part of our immune system that helps us struggle off infections in a selected and lasting method. In contrast to our physique’s first line of protection, which works rapidly however usually, adaptive immunity takes a bit longer to kick in however is way more exact. It includes two principal forms of immune cells: T-cells and B-cells. These cells not solely keep in mind previous infections but in addition react extra successfully if the identical pathogen invades once more. On this information, we’ll break down how adaptive immunity works, specializing in how T-cells and B-cells develop and contribute to our immune responses. Whether or not you’re interested by how your physique fights ailments or simply trying to study extra, this text provides you with a transparent understanding of how adaptive immunity protects you.
Introduction to Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive immunity, also referred to as acquired immunity, represents a classy protection system designed to acknowledge and get rid of particular pathogens or antigens. In contrast to innate immunity, which gives a broad and basic protection towards a variety of invaders, adaptive immunity gives focused responses and retains a reminiscence of earlier encounters with particular antigens. This reminiscence permits the immune system to reply extra quickly and successfully upon subsequent exposures to the identical pathogen.
Traits of Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive immunity is distinguished by a number of key traits:
- Specificity: This technique is very particular to particular person microbes and pathogens. It achieves this specificity via the various repertoire of antigen receptors on lymphocytes, which allows the immune system to exactly goal an enormous array of antigens.
- Reminiscence: Some of the distinctive options of adaptive immunity is its means to recollect prior exposures to antigens. After the immune system encounters a pathogen, it generates reminiscence cells that persist long-term. Upon reexposure to the identical antigen, these reminiscence cells facilitate a extra fast and strong immune response.
- Enhanced Response: Following an preliminary publicity to a pathogen, the immune response turns into faster and more practical throughout subsequent encounters. This enhancement is as a result of reminiscence element, which permits for a extra environment friendly clearance of the pathogen.
Adaptive immunity usually takes longer to develop into activated in comparison with innate immunity however gives a extra enduring safety. The immune system makes use of two principal branches to attain this: cell-mediated immunity and humoral immunity.
T-Cell Differentiation and Operate
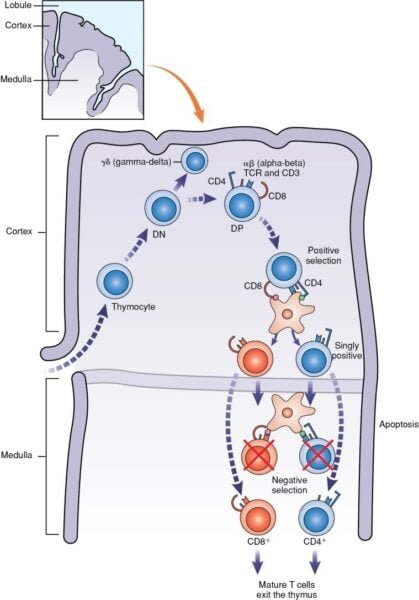
T-Cell Improvement
T cells originate from hematopoietic stem cells within the bone marrow and mature within the thymus. Their growth is a multi-stage course of:
- Double Unfavorable (DN) Stage: At this early stage, thymocytes lack each CD4 and CD8 floor markers.
- Double Constructive (DP) Stage: Thymocytes specific each CD4 and CD8 markers as they bear gene rearrangement for the T-cell receptor (TCR).
- Single Constructive (SP) Stage: Thymocytes that efficiently rearrange their TCR genes and cross choice processes specific both CD4 or CD8, however not each.
Throughout their time within the thymus, thymocytes undergo a number of essential processes:
- Gene Rearrangement: Thymocytes bear rearrangement of genes coding for the beta chain of the TCR, leading to a singular antigen-binding website.
- Constructive Choice: Thymocytes are chosen primarily based on their means to reasonably acknowledge MHC molecules on stromal cells within the thymic cortex. Profitable thymocytes proceed to the following stage.
- Unfavorable Choice: Thymocytes that both fail to bind MHC molecules or bind too strongly to self-antigens bear apoptosis, making certain self-tolerance and stopping autoimmunity.
T-Cell Subsets and Capabilities
T cells may be categorized into a number of subsets primarily based on their floor markers and capabilities:
- Helper T Cells (CD4+): These cells help different immune cells by secreting cytokines. They’re additional divided into:
- Th1 Cells: Produce cytokines akin to IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-β. They’re important for activating cytotoxic T cells (Tc) and macrophages to fight intracellular pathogens.
- Th2 Cells: Secrete interleukins IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, and IL-13. Th2 cells assist B cells produce antibodies and are concerned within the clearance of extracellular parasites and allergic responses.
- Th17 Cells: Produce IL-17 and IL-22, recruiting granulocytes to struggle bacterial infections and doubtlessly contributing to autoimmune ailments.
- Regulatory T Cells (Tregs, CD4+CD25+): These cells assist keep immune tolerance by suppressing the immune response to self-antigens and innocent antigens. They secrete inhibitory cytokines to modulate the exercise of different T-cell populations.
- Cytotoxic T Cells (CD8+): These cells are specialised in killing cells contaminated with intracellular pathogens. They launch cytotoxic granules containing perforin and granzymes and might induce apoptosis in goal cells via the engagement of demise receptors.
B-Cell Differentiation and Operate
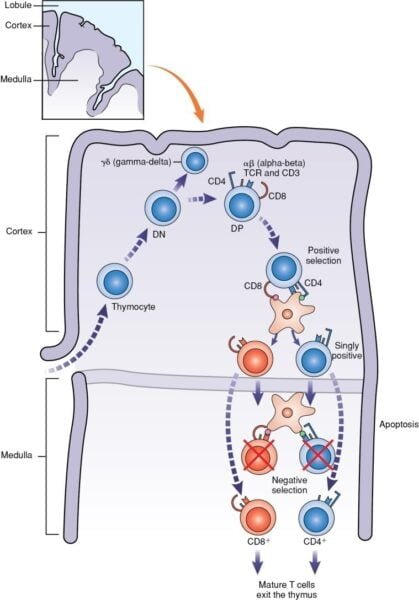
B-Cell Improvement
B cells additionally originate from hematopoietic stem cells however mature within the bone marrow. Their growth contains a number of phases:
- Antigen-Unbiased Part: This happens within the bone marrow and includes development via:
- Professional-B Cells: Start to rearrange immunoglobulin genes.
- Pre-B Cells: Categorical a pre-B cell receptor (pre-BCR) with a heavy chain and a surrogate gentle chain.
- Immature B Cells: Full rearrangement of sunshine chain genes, expressing a practical B-cell receptor (BCR) on their floor.
- Mature B Cells: Have practical BCRs and are able to migrate to secondary lymphoid organs.
Throughout growth, B cells bear gene rearrangement to supply a various repertoire of antibody specificities. This course of contains the creation of variable areas via somatic recombination, important for recognizing a broad vary of antigens.
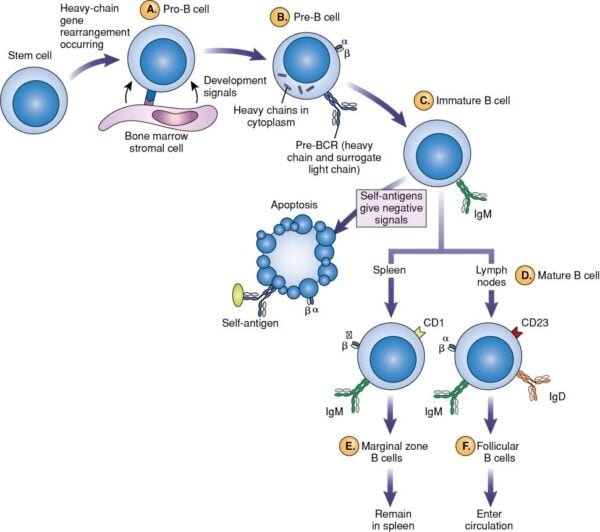
Antigen-Dependent Part
Upon encountering an antigen, B cells enter the antigen-dependent part:
- Activation and Proliferation: B cells are activated upon binding to their particular antigen. This activation typically requires help from Th cells, particularly for T-dependent antigens. B cells then proliferate and differentiate.
- Differentiation: Activated B cells differentiate into:
- Plasma Cells: Specialised in producing and secreting massive portions of antibodies. They’re present in bone marrow and peripheral lymphoid organs, having plentiful cytoplasmic immunoglobulins (Ig) however little floor Ig.
- Reminiscence B Cells: Persist long-term and might reply extra quickly and successfully to subsequent exposures to the identical antigen.
Position of T Cells in Adaptive Immune Response
T cells are essential within the adaptive immune response via their interactions with antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and their differentiation into varied subsets:
- APCs: These embody dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. APCs course of and current antigen fragments to T cells through MHC molecules, which is crucial for initiating the adaptive immune response.
- T-Cell Activation: T cells flow into via the bloodstream, lymph nodes, and secondary lymphoid tissues in quest of APCs presenting particular antigen-MHC complexes. The interplay between the TCR and antigen-MHC complicated, together with further co-stimulatory indicators, results in T-cell activation and proliferation.
Position of B Cells in Adaptive Immune Response
B cells are central to the humoral immune response:
- Antigen Recognition and Binding: B cells have membrane-bound immunoglobulins that act as antigen receptors. Upon encountering an antigen, B cells bear activation and differentiation.
- Manufacturing of Antibodies: Activated B cells differentiate into plasma cells that secrete antibodies. These antibodies neutralize pathogens, promote phagocytosis, and activate the complement system.
T-Dependent and T-Unbiased Antigens
- T-Dependent Antigens: These antigens require the assistance of T helper cells for B-cell activation. B cells reply by producing varied antibody lessons (e.g., IgG) and producing reminiscence cells. The antigen specificity of the BCR improves through the immune response via a course of often known as affinity maturation.
- T-Unbiased Antigens: These antigens can activate B cells with out T cell assist. They usually have repetitive constructions that cross-link BCRs, resulting in the manufacturing of IgM antibodies. Nevertheless, T-independent responses usually don’t generate reminiscence cells.
Scientific Implications and Advances
Autoimmune Ailments
Failures in adaptive immunity can result in autoimmune ailments, the place the immune system mistakenly targets self-tissues. Examples embody:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Characterised by persistent irritation of the joints.
- Sort 1 Diabetes: Includes the destruction of insulin-producing cells within the pancreas.
Immunodeficiencies
Immunodeficiencies outcome from defects in adaptive immunity, resulting in elevated susceptibility to infections. Examples embody:
- Extreme Mixed Immunodeficiency (SCID): A genetic dysfunction resulting in a extreme lack of each B and T cells.
- HIV/AIDS: Human Immunodeficiency Virus targets CD4+ T cells, resulting in acquired immunodeficiency.
Advances in Immunotherapy
Current advances in immunology have led to modern therapies akin to:
- CAR-T Cell Remedy: Includes engineering sufferers’ T cells to precise chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) focusing on most cancers cells.
- mRNA Vaccines: Make the most of messenger RNA to instruct cells to supply antigens, resulting in an immune response. This know-how has been notably utilized in COVID-19 vaccines.
Conclusion
Adaptive immunity is a posh and extremely specialised system that gives focused and long-lasting safety towards particular pathogens. By means of the intricate processes of T-cell and B-cell growth, activation, and differentiation, the adaptive immune system ensures a exact response to infections and the flexibility to recollect earlier encounters. Understanding these mechanisms not solely enhances our data of immune operate but in addition informs the event of novel therapies and vaccines, highlighting the essential position of adaptive immunity in sustaining well being and combating illness.
References
- Janeway, C. A., Travers, P., Walport, M., & Shlomchik, M. J. (2001). Immunobiology: The Immune System in Well being and Illness (fifth ed.). Garland Science.
- Murphy, Okay., & Weaver, C. (2016). Janeway’s Immunobiology (ninth ed.). Garland Science.
- Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, Okay., & Walter, P. (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). Garland Science.
- Kumagai, Y., & Takeuchi, O. (2014). “The Position of Sample Recognition Receptors in Innate Immunity and Adaptive Immunity.” Present Opinion in Immunology, 26, 1-8.
- Banchereau, J., & Steinman, R. M. (1998). “Dendritic Cells and the Management of Immunity.” Science, 296(5573), 294-298.
- Nijmegen, R. M., & Tanaka, T. (2020). “The Improvement and Operate of Regulatory T Cells.” Annual Overview of Immunology, 38, 177-204.
- Galli, S. J., Nakae, S., & Tsai, M. (2005). “Mast Cells within the Improvement of Allergic Illness.” Nature Critiques Immunology, 5(7), 573-585.
- Sok, D., & Burton, D. R. (2018). “Current Advances in Antibody-Primarily based Therapies.” Nature Critiques Drug Discovery, 17(6), 441-458.