There may be little or no doubt that Earth is getting hotter, and that this warming is a results of human-driven gases within the environment that retailer warmth and redirect it towards our planet’s floor. And Earth is not the one planet to have skilled this so-called “greenhouse impact.”
Venus is the most well liked planet within the photo voltaic system and is also known as Earth’s “evil twin.” The 2 planets are comparable in dimension and mass, with Venus solely barely extra diminutive than Earth. They’re additionally comparatively comparable of their distances from the solar, and even began off trying remarkably comparable to one another. Venus additionally has volcanoes like Earth, although it is not clear if they’re nonetheless energetic.
But one thing appears to have gone drastically improper within the growth of Venus, leaving it fairly hellish and inhospitable. There’s a good likelihood that “one thing” is an excessive runaway greenhouse impact, the consequence of an overabundance of atmospheric greenhouse gases.
For the reason that Seventies, satellites stationed in house have been very important in gathering an image of how Earth is being impacted by international warming — and this warming is attributable to the greenhouse impact. People are pumping growing quantities of greenhouse gases into the environment because of the burning of fossil fuels and, in flip, are forcing the planet to warmth up far quicker than it ought to.
Nonetheless, as warnings are available from house businesses like NASA and the European Area Company concerning the modifications Earth is experiencing due to this greenhouse impact, a good starker and extra excessive warning in regards to the greenhouse impact could also be coming from a world away from Earth. It could possibly be coming from Venus. The causes of this greenhouse impact on Venus and Earth are completely different, to be clear. On Venus, the impact was pure and sure the results of extreme volcanism tens of millions or billions of years in the past — on Earth, it’s the results of humankind’s burning of fossil fuels.
Nonetheless, that does not imply Venus does not have classes to impart about local weather change and the necessity to stymie the move of greenhouse gases into the environment.
“Venus is actually a great instance of 1 extremity of the greenhouse impact run amok,” Eryn Cangi, Analysis scientist on the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Area Physics, College of Colorado Boulder, instructed Area.com. “Venus is exclusive in our photo voltaic system in plenty of methods. In some ways, it is just like Earth but in addition very completely different. It is also one in all only a few objects in our photo voltaic system with a considerable environment, and it is by far the one with the thickest, hottest, most intense environment.
“We are able to study terrestrial Earth-like planets by observing and finding out Venus and decoding it as an excessive case of what can occur.”
Associated: Venus’ environment: Composition, clouds and climate
What makes Venus so excessive?
The key variations between Earth and Venus largely come right down to the planets’ differing atmospheres. Venus’ environment on the floor is 90 bars, which signifies that it’s 90 occasions as thick as Earth’s environment. Which means, on the floor of Venus, there’s a strain just like what’s discovered within the ocean at a depth of round 2,550 toes (777 meters).
As you may think, for a planet experiencing a runaway greenhouse impact, Venus can also be far hotter than Earth. The most well liked temperature ever recorded on the floor of our planet was 134.1 levels Fahrenheit (56.7 levels Celsius) on the aptly named Furnace Creek Ranch in Dying Valley, California on July 10, 1913.
Venus makes this appear to be a winter stroll within the park.
Temperatures on Earth’s evil twin are estimated to succeed in round 870 levels Fahrenheit (465 levels Celsius), which is sizzling sufficient to soften lead. You might discover comparable temperatures right here on Earth — however provided that you have been to climb right into a pizza oven.
“This sizzling, thick environment means Venus cannot have any liquid water on the floor right now, not like Earth. However now we have proof that Venus has misplaced big quantities of water over its historical past sufficient to counsel that historic Venus might need had an identical quantity of water as Earth does right now,” Cangi mentioned. “Nonetheless, we do not know if that water was ever within the liquid kind — it could have solely existed as steam within the environment.”
The second planet from the solar, Venus, is nearer to our star than Earth is, so it’s pure to count on it to be hotter. However Venus orbits the solar at a distance of round 70% of that between Earth and the solar, which is not that a lot nearer. Mercury is definitely a lot nearer to the solar than Venus, orbiting at a distance equal to round 33% of the gap between our planet and the solar — but temperatures on the closest planet to the solar attain 800 levels Fahrenheit (465 levels Celsius).
So, there should be some purpose behind Venus’ warmth aside from its proximity to the solar. And, nicely, it seems that the thriller of why Venus diverged from Earth in its early historical past, and the puzzle of how it may be hotter than the closest planet to the solar, each have the identical answer: a runaway greenhouse impact.
A greenhouse in hell
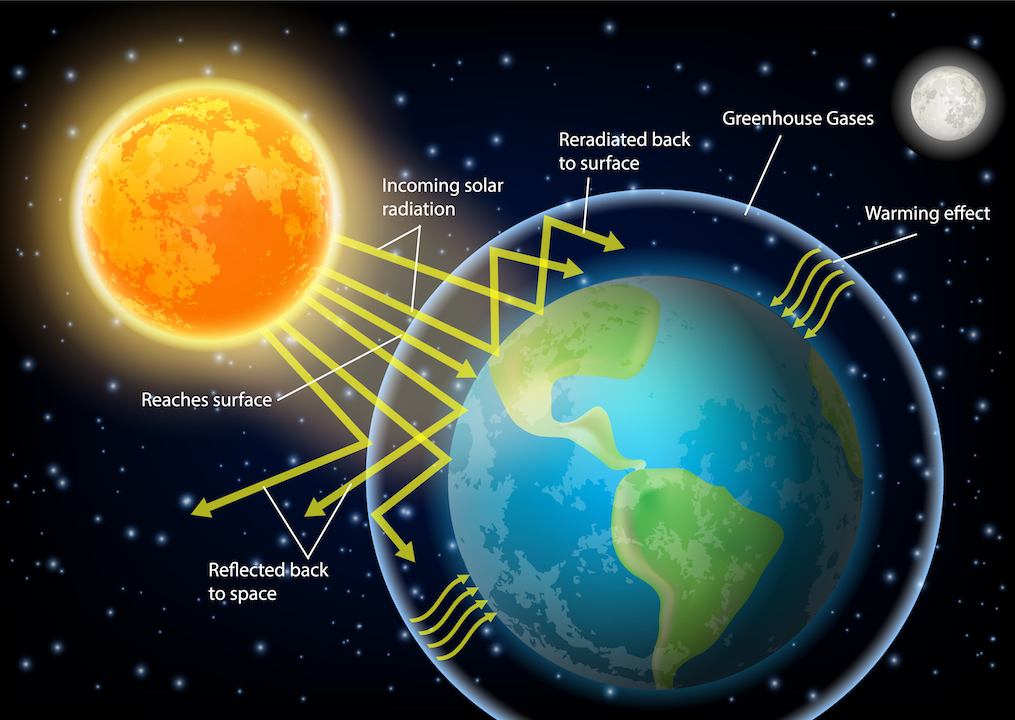
Earth and Venus obtain warmth from photo voltaic radiation, however a few of that radiation will get radiated again into house when daylight is mirrored again by clouds or ice. The planet’s floor absorbs the warmth that isn’t radiated again from house.
Sure gases in a planet’s environment can lure warmth, affecting how a lot power that planet loses again to house. They’re referred to as greenhouse gases.
Greenhouse gases can bounce the warmth round in all instructions, that means a few of the warmth inevitably will get directed again to the floor of the planet, thereby elevating the planet’s total temperature. The principle greenhouse gases are water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide, that are launched by the burning of fossil fuels.
With out this greenhouse impact, it’s estimated that Earth’s floor temperature can be tens of levels decrease. With out the greenhouse impact on Venus, the temperature on the second planet from the solar can be an estimated 700 levels (390 levels C) cooler.
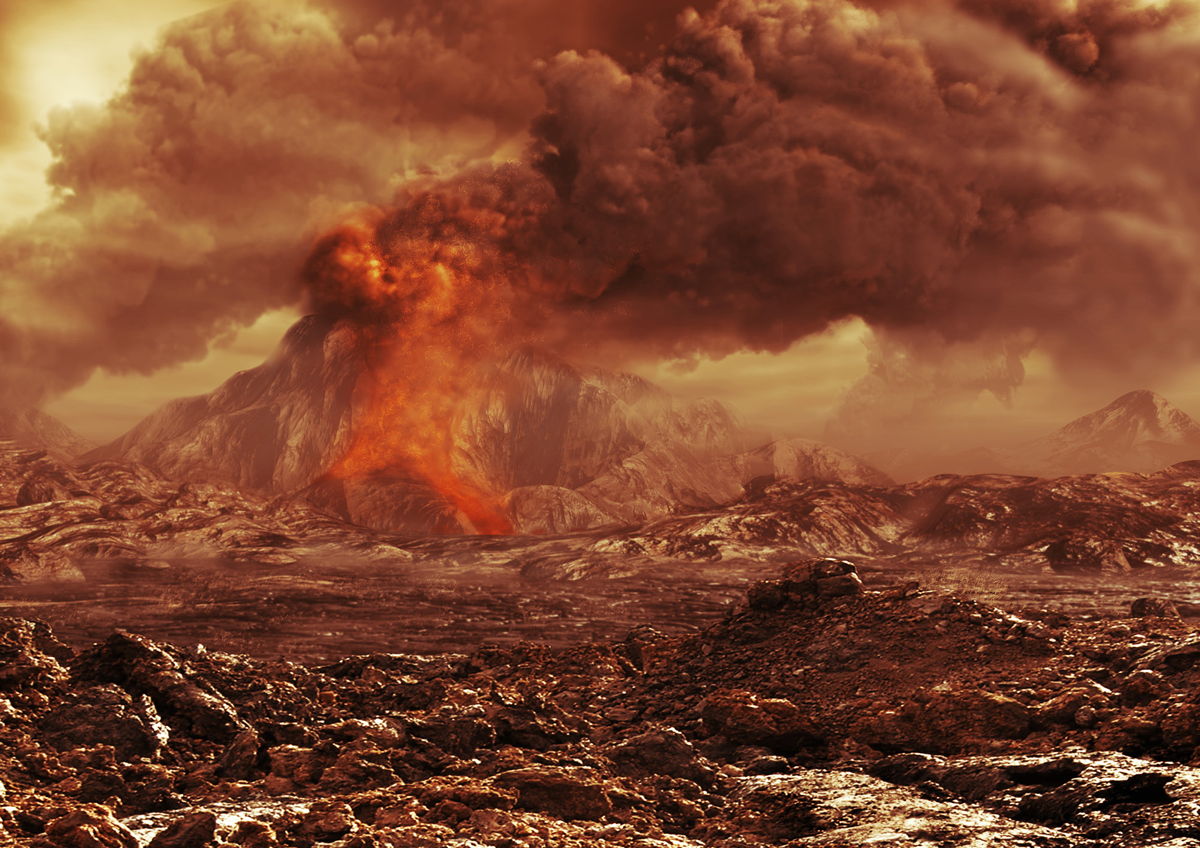
Scientists aren’t precisely certain when this greenhouse impact grabbed Venus in a stranglehold, with estimates starting from 3 billion years in the past to 250 million years in the past. Fairly how this “Nice Local weather Transition” took Venus from probably liveable to a hellish wasteland can also be debated, however one chance is {that a} huge bout of volcanism higher than something ever seen on Earth ripped open the crust of Venus and launched huge quantities of greenhouse gases, significantly carbon dioxide.
As temperatures on Venus soared, liquid water would have boiled away, with water vapor becoming a member of different huge quantities of greenhouse gases within the Venusian environment, inflicting increasingly warmth to be trapped, additional driving up temperatures. This might have brought on a suggestions loop of increasingly water evaporating, and extra warmth being trapped, making a “runaway greenhouse impact.”

Although Venus is a placing instance of the greenhouse impact, it should not function a “crystal ball” to foretell the way forward for the Earth. The scenario on our neighboring planet is completely different from that on Earth.
“I feel it is fairly unlikely that Earth would find yourself the identical as Venus, which has 90 Earth atmospheres value of carbon dioxide. On Earth, carbon dioxide is barely 0.04% of the environment, and the orbital mechanics additionally play into the distinction,” Cangi defined. “That does not imply we should not fear about local weather change on Earth. Many societal and power system modifications that may assist mitigate anthropogenic [human-caused] local weather change are additionally good for the well being of ourselves, our societies and our economies.”

The unlikeliness of Earth in following Venus down the freeway to local weather hell additionally does not imply we won’t be taught something in regards to the local weather dilemma dealing with our planet by investigating Venus. A number of upcoming missions will go to Venus in an try and unlock the secrets and techniques of its violent situations and its transformation into the photo voltaic system’s most fearsome world.
NASA’s Deep Environment Venus Investigation of Noble Gases, Chemistry and Imaging (DAVINCI) spacecraft shall be of specific curiosity. Set to succeed in Venus within the late 2030s, DAVINCI would be the first spacecraft to drop a probe by way of the dense environment of this hellish world, gathering knowledge about its construction and composition. Although this probe is not predicted to outlive its fall, scientists are ready for the likelihood that it might briefly survive the crushing atmospheric pressures of Venus to collect knowledge instantly from the Venusian floor for humanity.
“I am fascinated by something we do not perceive, so different planets are excellent! Venus is particularly fascinating as a result of there’s nonetheless a lot we do not know. I am very excited to be taught extra in regards to the floor of Venus from upcoming missions, particularly the extent of present-day volcanism,” Cangi concluded. “Under the clouds, we all know so little in regards to the decrease environment. I am very fascinated by what makes planets liveable or not and the way that may change over time, so Venus is a good case research and instance of a planet that might have as soon as been liveable however is not right now.”
Although this might reveal extra in regards to the greenhouse impact on Venus, for us to be taught actually be taught extra about local weather change and the greenhouse impact’s influence on our personal planet, we rely on house monitoring and the sort of expertise World Area Week will spotlight over the subsequent few days.
This text is a part of a particular sequence by Area.com in honor of World Area Week 2024, which runs from Oct. 4 to Oct. 10. Test again every day for a brand new function about how house expertise intersects with local weather change.

