Mobile biology delves into the intricate methods cells keep their inside setting, work together with their environment, and regulate their features. Important to those processes are passive and lively transport mechanisms. These methods management the motion of important substances into and out of cells. This text explores these mechanisms, specializing in tonicity, diffusion, osmosis, and the function of membrane proteins in lively transport.
Tonicity and Its Affect on Cells
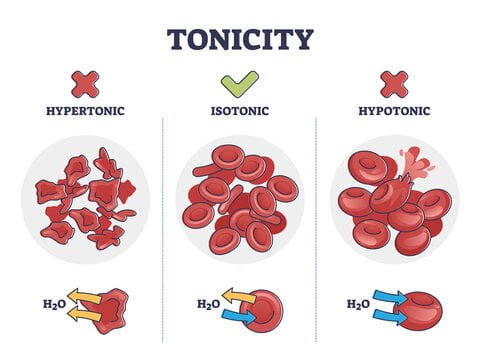
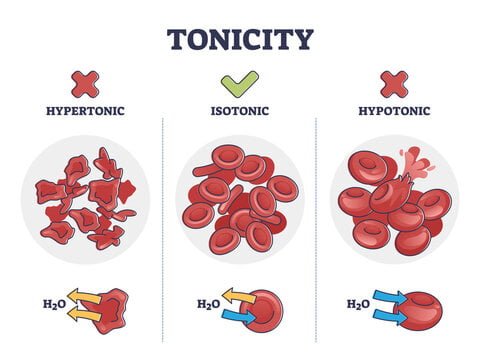
Tonicity describes how the focus of solutes in an answer influences water motion throughout a cell membrane. Understanding tonicity is essential for greedy how cells keep their form and performance in varied environments.
Hypotonic Options
A hypotonic answer has a decrease solute focus in comparison with the within of the cell, leading to a better focus of water molecules outdoors the cell. This imbalance impacts cells in a number of methods:
- Osmotic Strain Gradient: Water strikes into the cell as a result of osmotic stress gradient created by the decrease solute focus outdoors. Osmosis entails water touring by way of a semi-permeable membrane from areas of decrease solute focus to increased solute focus. Though the cell membrane permits water passage, it restricts solute motion.
- Cell Swelling: As water enters the cell, it accumulates within the cytoplasm, inflicting the cell to develop. This swelling will increase inside stress and might stretch the cell membrane.
- Lysis Danger: Persistent hypotonic situations can result in extreme water entry, leading to inside stress which will trigger the cell to burst or lyse, thus releasing its contents into the extracellular house.
Isotonic Options
An isotonic answer matches the solute focus of the cell’s cytoplasm. The first traits of isotonic options embrace:
- Balanced Osmotic Strain: On this setting, the osmotic stress inside and outdoors the cell is equal. Subsequently, water motion into and out of the cell is balanced, with no web change in water quantity.
- Secure Cell Quantity: As a result of balanced water motion, the cell retains its regular form and quantity. Isotonic options are essential in medical therapies, similar to intravenous fluids, to forestall mobile swelling or shrinkage.
Hypertonic Options
A hypertonic answer comprises a better focus of solutes in comparison with the within of the cell. The consequences on cells embrace:
- Osmotic Strain Gradient: Water exits the cell to the hypertonic ECF, pushed by the upper solute focus outdoors. This motion helps equalize solute concentrations throughout the membrane.
- Cell Shrinkage: Water loss causes the cell to shrink, a course of often known as crenation. This shrinkage can impair cell perform and, if extreme or extended, might result in mobile harm.
- Medical Makes use of: Hypertonic options can be utilized therapeutically to deal with situations similar to edema by drawing extra fluid out of tissues.
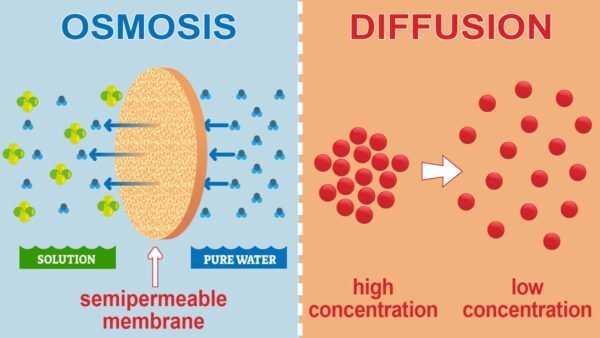
Osmosis and diffusion are elementary passive transport mechanisms that contain totally different substances and processes.
Diffusion
- Definition: The method of Diffusion is the motion of solutes from an space of upper focus to an space of decrease focus. This course of continues till the solute focus reaches equilibrium.
- Course of: Solute particles transfer freely throughout the plasma membrane whether it is permeable to them. This mechanism doesn’t require vitality (ATP). For example, the unfold of a fragrance scent in a room demonstrates diffusion.
Osmosis
- Definition: Osmosis is a sort of diffusion targeted on water motion. It happens from areas of decrease solute focus (hypotonic) to areas of upper solute focus (hypertonic) by way of a semi-permeable membrane.
- Course of: Osmosis balances water concentrations on both facet of the membrane. In isotonic options, water motion is balanced. Nonetheless, in hypotonic and hypertonic options, water adjusts to stability solute concentrations.
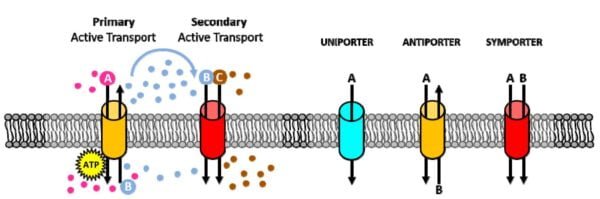
Energetic Transport by way of Membrane Proteins
Energetic transport is important for shifting substances throughout cell membranes towards their focus gradients. In contrast to passive transport, which depends on pure gradients, lively transport requires vitality within the type of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Major Energetic Transport
- Sodium-Potassium Pump: This pump is significant for sustaining sodium and potassium ion gradients throughout the cell membrane. It transports three sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell per ATP molecule hydrolyzed. This course of creates important gradients for varied mobile features, together with nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction.
Secondary Energetic Transport
- Mechanism: Secondary lively transport not directly makes use of ATP by counting on the gradients established by main lively transport. For instance, the sodium gradient generated by the sodium-potassium pump helps drive the transport of gear like glucose towards their gradients.
- Co-Transport: This mechanism typically entails co-transporters that use the sodium ion motion down its gradient to maneuver different substances towards their gradients.
Kinds of Membrane Pumps
- Uniport Pumps: These transport a single substance in a single route throughout the membrane. For instance, the calcium pump helps keep low intracellular calcium ranges by shifting calcium ions out of the cell.
- Symport Pumps: These transfer two or extra substances in the identical route. An instance is the sodium-glucose symporter, which transports each sodium ions and glucose into the cell concurrently.
- Antiport Pumps: These transport substances in reverse instructions. The sodium-potassium pump is a traditional antiport instance, shifting sodium ions out and potassium ions into the cell.
Energetic Transport by way of Vesicles
When substances are too giant or too polar to go by way of the plasma membrane immediately, cells use vesicular transport.
Vesicular Transport
- Vesicles: These are small, membrane-bound sacs that transport giant molecules or particles into or out of the cell. Vesicles can both fuse with the plasma membrane to launch their contents or kind from the membrane to internalize substances.
- Vitality Requirement: Vesicular transport is an lively course of requiring ATP to maneuver vesicles and their contents throughout mobile membranes.
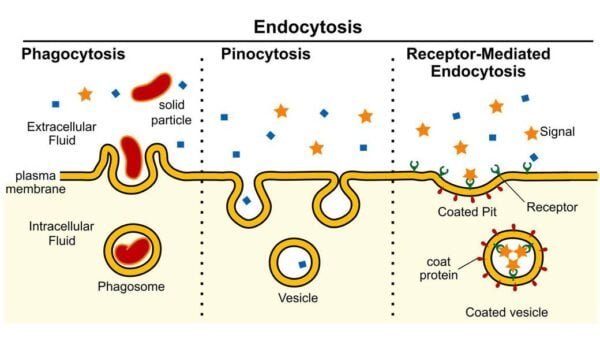
Endocytosis
- Phagocytosis: Usually termed “cell consuming,” this course of entails the engulfing of huge particles similar to micro organism or lifeless cells. The engulfed materials is enclosed in a phagosome, which subsequently fuses with lysosomes for digestion.
- Pinocytosis: Referred to as “cell consuming,” this course of entails the consumption of fluid droplets from the extracellular house. Small vesicles enclose the fluid, which is then processed contained in the cell.
- Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis: This particular sort of pinocytosis makes use of floor receptors to selectively internalize particular molecules, similar to hormones or ldl cholesterol. The binding of those molecules to their receptors triggers vesicle formation and internalization.
Exocytosis
- Course of: Exocytosis is the reverse of endocytosis. It entails vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane to launch their contents outdoors the cell. This course of is significant for the secretion of hormones, neurotransmitters, and different important molecules.
Conclusion
A complete understanding of passive and lively transport mechanisms is key in mobile biology. Passive processes, similar to diffusion and osmosis, rely on focus gradients and don’t require vitality. Conversely, lively transport processes, together with main and secondary transport, make the most of vitality to maneuver substances towards their gradients. Moreover, vesicular transport accommodates molecules too giant to go by way of the plasma membrane immediately.
These transport mechanisms are essential for sustaining mobile homeostasis, facilitating intercellular communication, and permitting cells to adapt to their environments. Mastering these ideas gives precious perception into the advanced and dynamic nature of mobile life.